In the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, where models often grapple with the paradox of progress - gaining new knowledge at the expense of the old - Google Research has introduced a groundbreaking paradigm that promises to bridge the gap between machine efficiency and human adaptability.
Announced on November 7, 2025, Nested Learning reimagines how AI systems acquire and retain information, treating them not as static networks but as dynamic, layered ecosystems of optimization. This approach tackles the notorious "catastrophic forgetting" problem head-on, enabling models to learn continuously without erasing prior skills.
At its core, Nested Learning posits that a single AI model is a "system of interconnected, multi-level optimization problems that are optimized simultaneously," rather than a monolithic entity trained through one overarching loop. Unlike traditional deep learning, where updates to parameters can overwrite established knowledge - like a student cramming for a new exam and blanking on last semester's material - Nested Learning integrates fresh data as nested layers within an existing structure. This creates a hierarchical "continuum memory system" (CMS), where memory isn't binary (short-term vs. long-term) but a spectrum of modules updating at varying frequencies.
How Nested Learning Mimics the Human Brain's Graceful Evolution
Imagine the human mind as a vast library, where new books don't displace the old ones but are shelved in interconnected annexes, cross-referenced for easy recall. Nested Learning operationalizes this metaphor through a structured hierarchy of learning levels, each governed by its own "context flow" and update rate. Inner levels - those handling immediate, high-frequency tasks like processing real-time input - update rapidly, while outer levels, storing foundational knowledge, evolve more slowly. This ordering prevents interference, allowing the model to compress and refine its internal representations without disruption.
Technically, the paradigm unifies a model's architecture (e.g., layers in a neural network) with its optimization algorithm (e.g., gradient descent). By defining an update frequency rate - how often each component's weights are adjusted - these interconnected optimization problems are ordered into "levels." This ordered set forms the heart of the Nested Learning paradigm. Backpropagation, for instance, is reframed as an associative memory module that maps data to errors, while attention mechanisms in transformers become tools for recalling token relationships across contexts.
To demonstrate, Google developed HOPE (Hierarchical Optimization for Persistent Evolution), a self-modifying architecture built as a variant of their earlier Titans model - a memory module that prioritizes "surprising" information. HOPE incorporates CMS to extend beyond the standard transformer's short-term sequence modeling and long-term feedforward storage, creating a fluid memory gradient. This bio-inspired design draws from early theoretical work, such as Jürgen Schmidhuber's 1992 paper on self-modifying neural networks, finally providing a practical framework for "learning how to learn."
The Superpowers Unlocked: Benefits That Redefine AI Capabilities
Nested Learning isn't just theoretical - it's a practical leap toward more resilient, intelligent systems.
.jpg) Here are the key advantages:
Here are the key advantages:
1. Endless Learning Without Catastrophic Forgetting
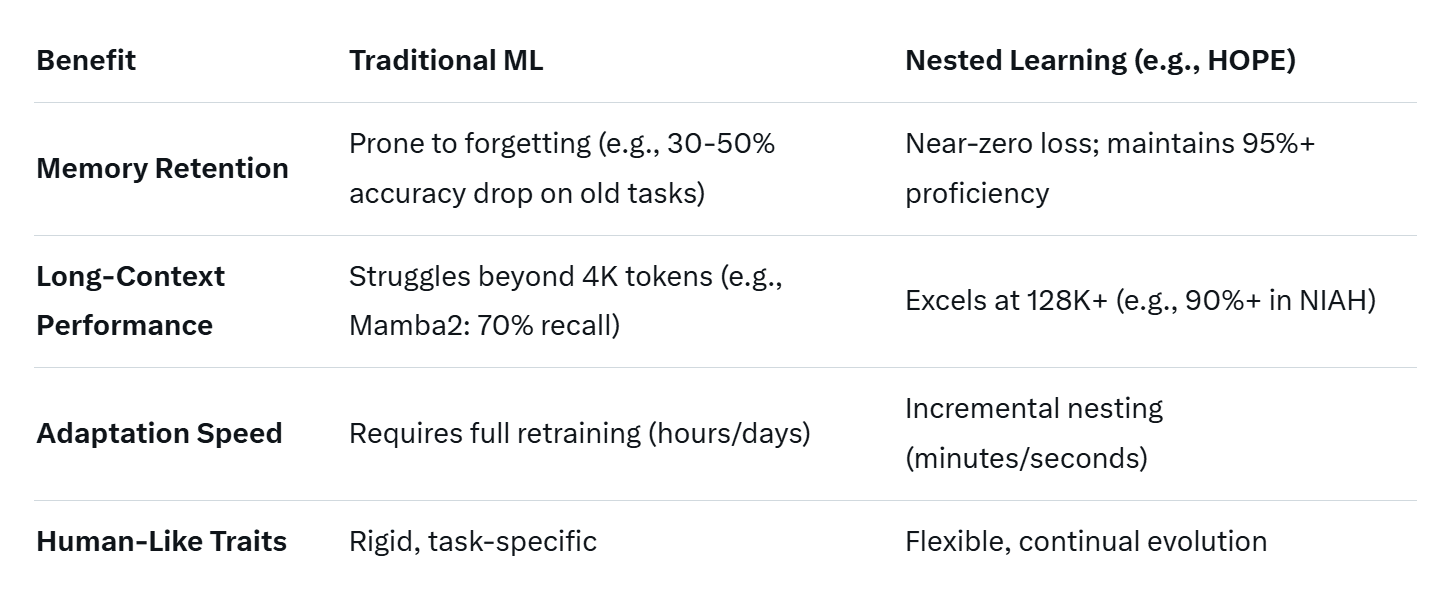
Traditional models suffer from "catastrophic forgetting," where fine-tuning on new data erases old competencies, necessitating costly retraining from scratch. Nested Learning circumvents this by nesting updates: new knowledge forms sub-models that link to prior ones, preserving the hierarchy. In HOPE's tests on language modeling tasks, it achieved lower perplexity (a measure of prediction error) compared to baselines like Titans and Samba, while maintaining proficiency across sequential learning phases. This means AI could theoretically "learn infinitely," adapting to evolving datasets without performance cliffs.
2. Contextual Intelligence and Adaptive Behavior
 By distinguishing update levels, models gain nuanced awareness of their operational "mode." For long-context reasoning—crucial for tasks like summarizing lengthy documents or multi-turn conversations - HOPE excelled in Needle-In-A-Haystack (NIAH) benchmarks. These tests hide a "needle" (e.g., a passkey) in a "haystack" of up to 128,000 tokens; HOPE outperformed Titans, TTT, and Mamba2 across varying difficulties, retrieving information with up to 20% higher accuracy in hard scenarios. This contextual depth makes AI more "human-like," switching seamlessly between creative brainstorming and precise fact-checking.
By distinguishing update levels, models gain nuanced awareness of their operational "mode." For long-context reasoning—crucial for tasks like summarizing lengthy documents or multi-turn conversations - HOPE excelled in Needle-In-A-Haystack (NIAH) benchmarks. These tests hide a "needle" (e.g., a passkey) in a "haystack" of up to 128,000 tokens; HOPE outperformed Titans, TTT, and Mamba2 across varying difficulties, retrieving information with up to 20% higher accuracy in hard scenarios. This contextual depth makes AI more "human-like," switching seamlessly between creative brainstorming and precise fact-checking.
3. A Step Closer to Biological Cognition
Humans don't rebuild neural pathways from zero with every lesson; neuroplasticity allows gradual, multi-scale adaptation. Nested Learning emulates this, fostering recursive self-improvement. It reframes AI as a living hierarchy of learning systems, not a frozen network, enabling deeper computational expressivity. Early results suggest applications in meta-learning, where models optimize their own optimizers, paving the way for artificial general intelligence (AGI).
Also read:
- The AI Arms Race Heats Up: Anthropic Uncovers China-Sponsored Autonomous Cyberattacks Using Claude Code
- The Startup We Deserve: How Tuute Turned Fart Logging into a Global Phenomenon
- Disney's $1 Billion Content Spending Surge in 2026: A Sports-Fueled Bet on Streaming Supremacy
- SEO for Doctors
Challenges, Comparisons, and the Road Ahead
 While promising, Nested Learning isn't without hurdles. Designing optimal update hierarchies requires careful tuning, and scaling to massive models like GPT-scale LLMs demands computational resources.
While promising, Nested Learning isn't without hurdles. Designing optimal update hierarchies requires careful tuning, and scaling to massive models like GPT-scale LLMs demands computational resources.
Compared to rivals - such as OpenAI's o1 series with its chain-of-thought reasoning or Anthropic's constitutional AI - Nested Learning stands out for its focus on intrinsic memory architecture over prompt engineering. It outperforms state-of-the-art on reasoning and recall but lags in raw speed for simple tasks, highlighting a trade-off for depth.
Looking forward, potential applications span healthcare (AI diagnosing evolving diseases without retraining), robotics (adapting to new environments mid-mission), and personalized education (tutors that remember every student's progress). Future work could integrate external memory or symbolic reasoning, expanding beyond language to multimodal domains.
Google's Nested Learning isn't merely an incremental upgrade - it's a paradigm shift that whispers of AI's maturation into something truly alive. By nesting knowledge like Russian dolls of cognition, it edges us closer to machines that don't just compute, but remember, adapt, and grow. As the field races toward AGI, this innovation reminds us: the future of intelligence lies not in bigger models, but smarter ones.
For more details, explore the official blog: Introducing Nested Learning.