Search results decide whether your site is seen or skipped. At the same time, most people now reach the web on a phone first. The meeting point of these facts gives us our topic: Does responsive design improve SEO? In short, yes—responsive pages make search engines and visitors happier. By following responsive design principles, websites adapt smoothly to different screen sizes and device types, ensuring a better user experience and improved crawlability. But the why and how matter. This article explores the link between responsive design and SEO, pointing out direct gains, hidden boosts, and simple steps you can use today.
What “Responsive Design” Really Means
 A responsive site changes shape to fit any screen—phone, tablet, laptop, or giant desktop. It does this with flexible grids, fluid images, and CSS breakpoints. No need for a separate “m-dot” mobile URL; one address serves all. That one-site approach matters for:
A responsive site changes shape to fit any screen—phone, tablet, laptop, or giant desktop. It does this with flexible grids, fluid images, and CSS breakpoints. No need for a separate “m-dot” mobile URL; one address serves all. That one-site approach matters for:
- User experience (UX): The page looks clean and easy to tap, read, and scroll.
- Maintenance: You update content once instead of in two places.
- Crawl efficiency: Search bots crawl a single version, saving their “crawl budget” for more pages on your domain.
If the layout shifts smoothly and text remains legible, you have the base of a responsive design.
Why Google Sees Mobile First
Since 2018, Google has used mobile-first indexing for most sites. That means its crawler judges your mobile view before your desktop view. When Googlebot finds pinch-zoom issues or slow load times on a phone, your rankings can suffer on all devices. Responsive design answers that risk by:
- Serving the same HTML to any device.
- Using CSS to adapt spacing, fonts, and navigation.
- Avoiding duplicate content that might arise from separate mobile URLs.
Because responsive equals one code base, search engines avoid indexing clashes and link dilution.
Direct SEO Benefits of Responsive Design
A. Faster Page Speed
Responsive techniques encourage lightweight resources—compressed images, modern formats, and code splitting. Faster sites lower bounce rate, which Google watches as a user-satisfaction signal.
B. Better Core Web Vitals Scores
Google’s Core Web Vitals measure Largest Contentful Paint, Cumulative Layout Shift, and First Input Delay. A clean, responsive layout can hit “green” scores by limiting unexpected shifts and trimming render-blocking files.
C. Reduced Duplicate Content
One URL per page keeps all backlinks in one place. The collected link equity pushes that single page higher in results.
D. Improved Crawl Budget
Bots spend less time deciding which mobile or desktop version to index. They use leftover time to explore deeper pages, letting more of your content appear in search.
E. Schema Consistency
When the same DOM powers every device, structured data markup stays uniform. That steady schema can unlock rich results like FAQs, breadcrumbs, or review stars.
Indirect SEO Boosts You May Not Notice at First
Responsive design also affects metrics that stand close to ranking factors:
- Lower Bounce Rate: A site that fits the screen keeps visitors from backing out.
- Longer Dwell Time: Easy reading and quick interaction hold attention.
- Higher Social Shares: Buttons are accessible on thumb-sized screens, leading to more shares and referral traffic.
- Better Conversion Rate: Forms that resize correctly get filled out more often, sending positive signals back through analytics tools tied to SEO reporting.
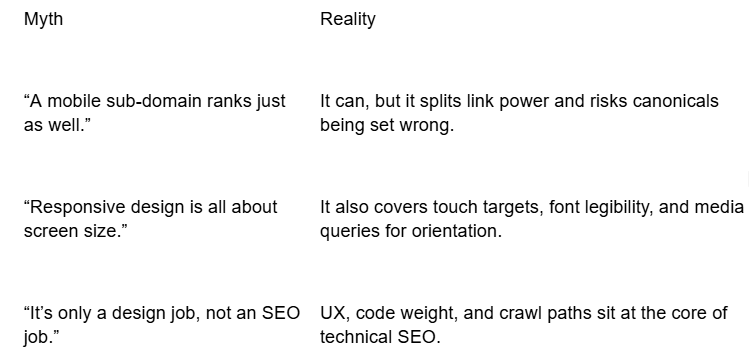
Common Myths Debunked
Best Practices for Marrying Responsive Design and SEO
 Use the checklist below as you plan or audit your site:
Use the checklist below as you plan or audit your site:
- Use a Flexible Grid, Not Fixed Pixels
Percent-based widths let columns expand or shrink without cutting off words.
- Set Viewport Meta Tag
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> tells the browser to match screen width.
- Compress and Serve Next-Gen Images
Formats like WebP, paired with srcset deliver sharp graphics at small file sizes.
- Load Critical CSS Inline, Defer the Rest
Render above-the-fold content fast, then stream extra styles.
- Avoid Intrusive Interstitials
Pop-ups that block content can hurt rankings, especially on mobile.
- Test with Lighthouse and Search Console
Run audits to catch layout shift, interactive delay, and indexing errors.
- Map Touch Targets
Buttons should be at least 48×48 CSS pixels, easing thumb taps and cutting accidental clicks.
- Craft Mobile-Friendly Structured Data
Mark up products, articles, and events the same on every device view.
- Monitor Core Web Vitals Over Time
Track field data, not just lab data, for real-world performance.
- Keep Content the Same Across Screens
Hiding text on mobile may look tidy but can appear like cloaking to bots.
Local Insight: Why Responsive Helps City Searches
When people type “near me” queries, Google mixes distance, relevance, and prominence. A responsive site shines in two of those areas:
- Relevance: Clear headings and readable copy keep users engaged, giving the algorithm good behavior signals.
- Prominence: Lower bounce and faster loads improve the metrics Google associates with quality.
Content Strategy Still Matters
Code cannot save thin or outdated copy. Once your layout adapts, fill it with content that:
- Answers clear questions.
- Uses natural language and long-tail phrases.
- Includes descriptive ALT text for images.
- Organizes ideas with H2 and H3 tags that echo search intent.
Pair that with a logical internal-link map. For instance, a service page might link out to a blog post that digs deeper, then loop back with a breadcrumb. That structure helps both users and crawlers navigate.
Voice Search and Emerging Screens
Smart speakers, car dashboards, and wearable displays continue to change how we reach information. A responsive mindset extends here, too:
- Semantic HTML5 helps screen readers and voice assistants parse your content.
- ARIA labels add clarity where icons replace words.
- Viewport-based units scale fonts on high-pixel-density watches and TVs.
By preparing your site for any context, you future-proof the SEO value you build today.
Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with good intent, some teams slip up:
- Blocking important resources (like CSS) in robots.txt, preventing Google from rendering the full page.
- Neglecting touch-friendly menus, leading to tiny links that frustrate mobile visitors.
- Overusing heavy JavaScript frameworks without server-side rendering, hurting Time to First Byte.
- Failing to test on real devices, relying only on browser tools that may not mimic network lag.
A single misstep can cancel many of the gains responsive design offers.
Measuring Success After the Switch
 Track these metrics before and after you launch a responsive redesign:
Track these metrics before and after you launch a responsive redesign:
- Organic sessions (mobile and overall)
- Average position for top keywords
- Bounce rate and dwell time
- Pages crawled per day in Google Search Console
- Core Web Vitals status in PageSpeed Insights
- Conversion rate for forms, calls, or sales
Set a three-month checkpoint. Responsive improvements often show early wins in usability data, followed by ranking lifts as Google re-crawls.
Final Thoughts
Responsive design is more than a cosmetic upgrade. It keeps your site usable on any screen and aligns with Google’s mobile-first lens. By merging best-practice coding with smart on-page SEO, you gain speed, clarity, and crawl efficiency—all ranking boosters. If you plan your layout with the same care you give your keywords, responsive design and SEO work together, not in silos. Embrace the synergy, monitor the data, and watch both user satisfaction and search visibility climb.
Also reed: SEO, Chatbots, Simulation: Enhancing Digital Strategies for 2025






