Hello!
Running a business is definitely not easy, but there are many tools that can help you stay on track, such as Gantt charts. Keep reading to learn more about what is a Gantt chart and how it can benefit your company.
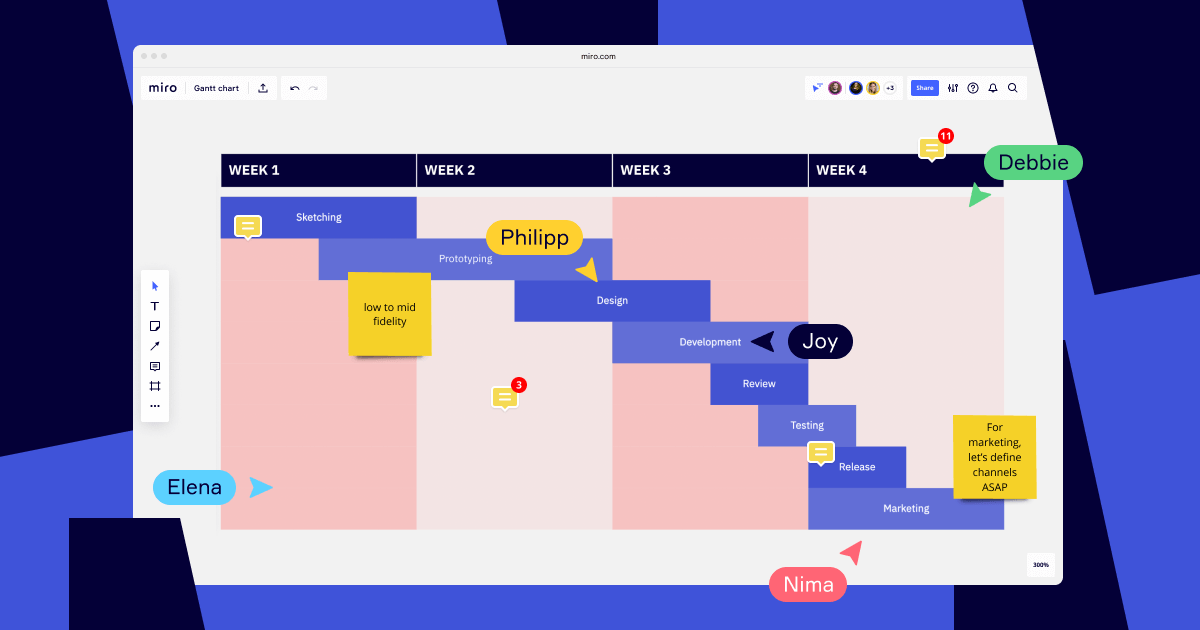
 A Gantt chart is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule and shows the relationship between tasks and their duration. The horizontal axis of the chart shows the time scale, while the vertical axis shows the different tasks that need to be completed. Each task is represented by a bar, with the bar length proportional to the duration of the task.
A Gantt chart is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule and shows the relationship between tasks and their duration. The horizontal axis of the chart shows the time scale, while the vertical axis shows the different tasks that need to be completed. Each task is represented by a bar, with the bar length proportional to the duration of the task.
There are many different types of Gantt charts, but they all share the same basic features. They allow you to visualize the start and finish dates of tasks, see how tasks are related to each other, and spot potential problems with the schedule. Gantt charts are also an effective way to communicate a project schedule to stakeholders. They are easy to understand and can help prevent misunderstandings about how a project is supposed to progress.
How Can Businesses Use Gantt Charts?
There are a number of ways businesses can use Gantt charts. First, businesses can use Gantt charts to plan and track projects. By plotting out each task and its dependencies, managers can ensure that each task is completed on time and that the project is completed on schedule. The percentage of completion for each task can be tracked, as well as the overall progress of the project. This allows managers to identify potential problems and address them before they become too serious.
Gantt charts are also a great way for businesses to establish timelines and deadlines, especially when there are multiple projects that need to be completed simultaneously. Gantt charts can help to ensure that all projects are completed on time and that none of them overlap or interfere with each other.
 Additionally, Gantt charts can be used to track milestones in a variety of ways. One way is to use the milestone as a point on the Gantt chart to track the progress of the project.
Additionally, Gantt charts can be used to track milestones in a variety of ways. One way is to use the milestone as a point on the Gantt chart to track the progress of the project.
This can be done by coloring in the milestone on the chart as it is completed. Another way to is to use the milestone as a line on the chart. This can be done by setting the milestone as the end date for a task and adding a start date to the task. This will create a line on the chart that will show how close the project is to the milestone.
Further, Gantt charts can be used to track resources by displaying when tasks are scheduled to begin and end, as well as what resources are needed to complete the tasks. This can help to identify potential bottlenecks in the project and help to adjust and optimize the schedule as needed.
Finally, Gantt charts can be used to forecast costs and assess risk. One common way to use Gantt charts for this purpose is to create a timeline for a project. This timeline can then be used to track the progress of the project and identify potential problems or delays that could impact the cost or schedule of the project. Additionally, Gantt charts can be used to create a risk assessment for a project, which can help to identify potential risks and estimate the likelihood and impact of those risks. Appropriate action can then be taken to mitigate risks.
How Do You Create A Gantt Chart?
To create a Gantt chart, businesses first need to list out all of the tasks that need to be completed as part of the project. They can then assign each task start date and end date. The chart will show the progress of the project as it unfolds, with different colors indicating whether a task is on schedule, behind schedule, or completed.
While there are a few different ways to create Gantt charts in Excel, this guide will walk through how to create a Gantt chart in Excel using a table and simple formulas. To get started, create a table with the following headings: “Task,” “Start Date,” “End Date,” “Duration,” and “Status.” Next, populate the table with your project tasks and corresponding start and end dates, duration, and status.
 Once your table is populated, you can create the Gantt chart by following these steps:
Once your table is populated, you can create the Gantt chart by following these steps:
- Select the data in the table, including the headings.
- Go to the Insert tab and click on the Chart button.
- In the Charts window, select the Bar chart type and click on the OK button. Excel will create the chart.
- To change the appearance of the chart, select any of the chart elements and use the Formatting options to change the color, font, size, and more.
- To add the task labels, select the Chart Elements button and then select the Axis Titles option.
- In the Axis Titles window, select the Primary Horizontal Axis and then select the Label option.
- In the Label window, select the Text option and then enter the text you want to appear as the axis label.
- Click on the OK button to close the window.
- You can also add the task start and end dates to the chart by selecting the Chart Elements button and then selecting the Data Points option.
- In the Data Points window, select the Series 1 option and then select the First Point of Series option.
- In the First Point of Series window, select the Horizontal Axis and then select the Date option.
- Click on the OK button to close the window.
- The final step is to add the task duration to the chart. To do this, select the Chart Elements button and then select the Data Labels option.
- In the Data Labels window, select the Series 1 option and then select the Duration option.
- Click on the OK button to close the window.
Conclusion
 The Gantt chart is now complete and can be further customized however you need. Some best practices to keep in mind in order to ensure its accuracy and usefulness include planning out the project in advance to determine the order of the tasks and the estimated completion date.
The Gantt chart is now complete and can be further customized however you need. Some best practices to keep in mind in order to ensure its accuracy and usefulness include planning out the project in advance to determine the order of the tasks and the estimated completion date.
Then, as the project progresses, update the Gantt chart to reflect the actual progress. Use the Gantt chart to identify any potential delays or problems and adjust the schedule as needed, keep track of the budget and expenses for the project and update the Gantt chart accordingly. Finally, be sure to celebrate milestones along the way.
Thank you!
Join us on social media!
See you!